Saturated Fatty Acids and Methyl Esters
The Author: Gerhard Knothe, National Center for Agricultural Utilization Research, Agricultural Research Service, U.S. Department of Agriculture, Peoria, IL, USA.
1H-NMR Spectroscopy of Fatty Acids and Their Derivatives
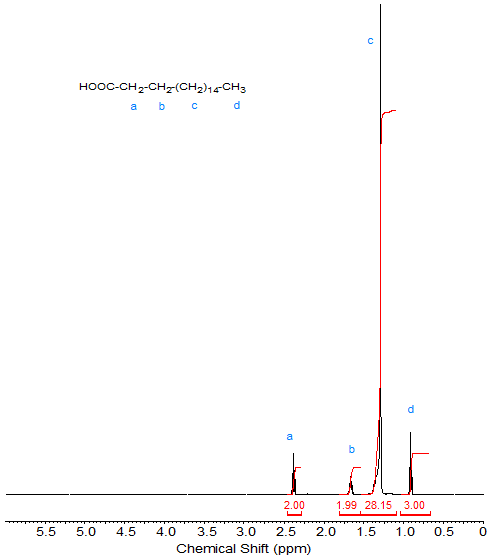
As mentioned in the Introduction to these web pages, because of their relative simplicity, the NMR spectra of stearic acid and methyl stearate will serve as references when discussing the "introduction" of other functional groups. The 1H-NMR spectrum (see Fig. 1) of stearic acid shows the following peaks:
- 2.35 ppm: CH2 α to COOH (C2 methylene; triplet);
- 1.65 ppm: CH2 of C3; multiplet
- 1.3-1.4 ppm: CH2 of C3-C16; theoretical integration value 28 (note the deviation in Fig. 1; this deviation is especially noticeable for the large number of CH2 protons in a long chain when assigning each proton an integration value of 1).
- 0.88 ppm: CH3 (C18 terminal methyl; triplet).
The proton of the carboxylic acid group is beyond the spectral range shown here (see Table 1 in the Introduction).
Figure 1. 1H-NMR spectrum of stearic acid.
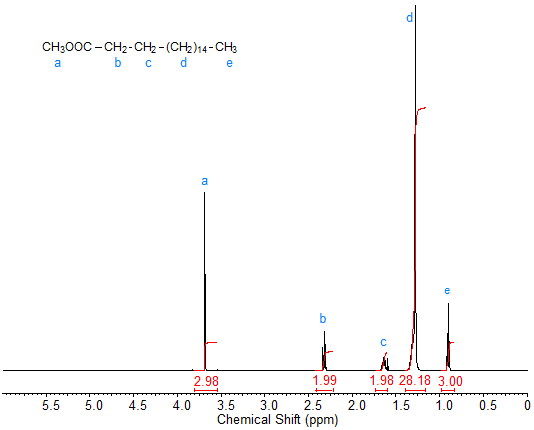
The 1H-NMR spectrum of methyl stearate (Fig. 2) is virtually identical to that of stearic acid except for the strong singlet peak caused by the methyl ester protons at about 3.7 ppm. This peak of the methyl ester protons can be useful for quantification purposes when monitoring reactions such as transesterification.
Figure 2. 1H-NMR spectrum of methyl stearate.
Obviously, in the spectra of other saturated fatty acids and methyl esters, the intensity and the integration value of the signals of the methylene moieties change. With the change in integration value, and if the integration is sufficiently accurate, fatty acid chain length can be determined, although this is of little practical value.
In This Section
- Introduction of NMR
- Saturated Fatty Acids and Methyl Esters
- Alkyl Esters Other than Methyl
- Glycerol Esters
- Non-Conjugated Double Bonds
- Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA)
- Acetylenic Fatty Acids and Derivatives
- Branched-Chain and Cyclic Fatty Acids
- Epoxy Fatty Acids
- Hydroxy and Hydroperoxy Fatty Acids
- Oxo Fatty Acids
- Fatty Alcohols
- Some Miscellaneous Fatty Acids
- Quantification by 1H-NMR
- The NMR Spectrum
- Alkanoic Acids
- Monoenoic Acids
- Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
- Non-Methylene-Interrupted Polyenoic Fatty Acids
- Acids with conjugated unsaturation
- Acetylenic and Allenic Acids and Esters
- Branched-Chain and Cyclic Fatty Acids
- Cyclic Fatty Acids
- Epoxides and Acyclic Ethers
- Hydroxy and Hydroperoxy Acids
- Oxo (Keto) Acids
- Acids, Esters (Alkyl, Glycerol, Waxes), Alcohols and Acetates, Amides, and Nitriles
- Esters of Glycerol and Other Polyhydric Alcohols
- Oils and Fats
- Regiospecific Analysis of Triacylglycerols