Fatty Alcohols
The Author: Gerhard Knothe, National Center for Agricultural Utilization Research, Agricultural Research Service, U.S. Department of Agriculture, Peoria, IL, USA.
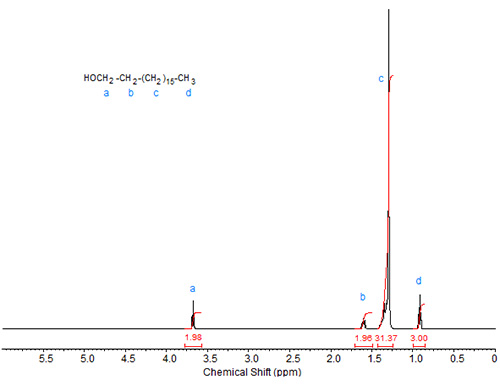
In comparison to the spectra of stearic acid and its esters, the spectrum of stearyl alcohol (Fig. 1) shows a triplet at about 3.65 ppm caused by the protons attached to C1. The protons at C2 are responsible for the multiplet (triplet of triplets) at about 1.6 ppm.
Figure 1. 1H-NMR spectrum of stearyl alcohol.
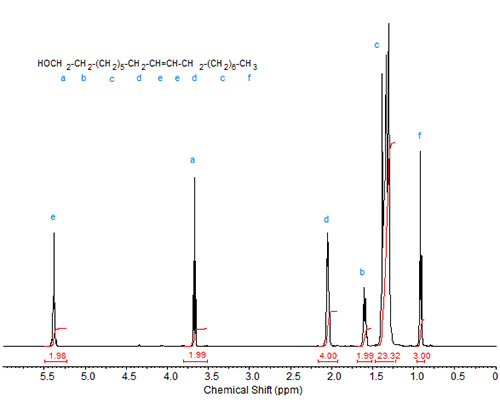
The spectrum of oleyl alcohol is shown in Figure 2. The major differences here are similar to those of methyl stearate vs. methyl oleate, namely presence of olefinic and allylic protons.
Figure 2. 1H-NMR spectrum of oleyl alcohol.
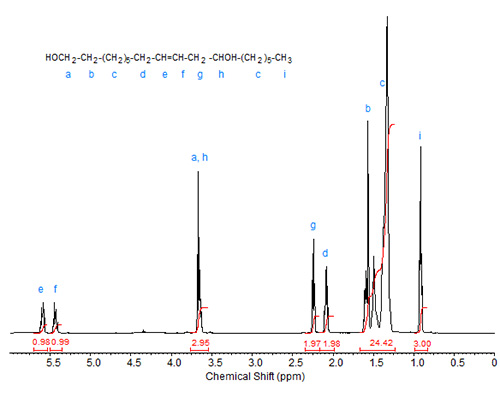
The spectrum of ricinoleyl alcohol is depicted in Figure 3. The peaks caused by the protons at C1 and C12 overlap here. Otherwise, the features of this spectrum are as discussed above for methyl ricinoleate.
Figure 3. 1H-NMR spectrum of ricinoleyl alcohol.
In This Section
- Introduction of NMR
- Saturated Fatty Acids and Methyl Esters
- Alkyl Esters Other than Methyl
- Glycerol Esters
- Non-Conjugated Double Bonds
- Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA)
- Acetylenic Fatty Acids and Derivatives
- Branched-Chain and Cyclic Fatty Acids
- Epoxy Fatty Acids
- Hydroxy and Hydroperoxy Fatty Acids
- Oxo Fatty Acids
- Fatty Alcohols
- Some Miscellaneous Fatty Acids
- Quantification by 1H-NMR
- The NMR Spectrum
- Alkanoic Acids
- Monoenoic Acids
- Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
- Non-Methylene-Interrupted Polyenoic Fatty Acids
- Acids with conjugated unsaturation
- Acetylenic and Allenic Acids and Esters
- Branched-Chain and Cyclic Fatty Acids
- Cyclic Fatty Acids
- Epoxides and Acyclic Ethers
- Hydroxy and Hydroperoxy Acids
- Oxo (Keto) Acids
- Acids, Esters (Alkyl, Glycerol, Waxes), Alcohols and Acetates, Amides, and Nitriles
- Esters of Glycerol and Other Polyhydric Alcohols
- Oils and Fats
- Regiospecific Analysis of Triacylglycerols