Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA)
Figures 1 to 3 depict the 1H-NMR spectra of three conjugated linoleic acid methyl esters, namely three isomers of methyl 9,11-octadecadienoate [cis,cis- (9Z,11Z); trans,trans- (9E,11E); cis,trans- (9Z,11E), respectively] that can serve as models for other CLA esters.
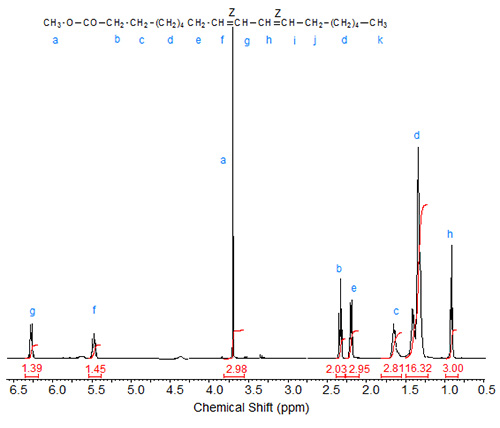
Figure 1. 1H-NMR spectrum of methyl 9(Z),11(Z)-octadecadienoate.
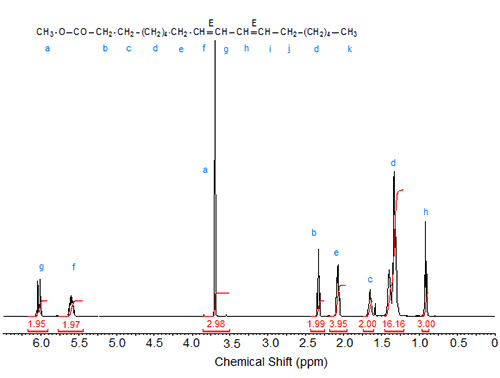
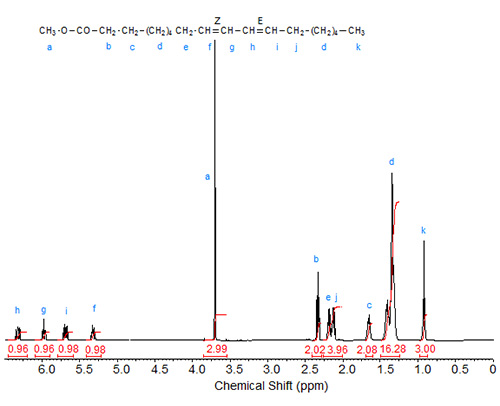
The characteristic shifts are relative to deuterochloroform (CDCl3) at 7.295 ppm and are given in Table 1.
| Table 1. Assignments of characteristic signals in the spectra of 9,11-octadecadienoic acid isomers (see Figs. 1 to 3): | |||||
| Allylic protons (C8, C13) | C9 | C10 | C11 | C12 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9Z,11Z | 2.08 | 5.47 | 6.27 | 6.27 | 5.47 |
| 9E,11E | 2.20 | 5.59 | 6.03 | 6.03 | 5.59 |
| 9Z,11E | 2.18 (cis), 2.13 (trans) | 5.32 | 5.97 | 6.34 | 5.69 |
Figure 2. 1H-NMR spectrum of methyl 9(E),11(E)-octadecadienoate.
Figure 3. 1H-NMR spectrum methyl 9(Z),11(E)-octadecadienoate.
The "inner" olefinic protons at C10 and C11 are shifted downfield compared to the "outer" olefinic protons at C9 and C12. Also, in accordance with the above discussion on oleic acid vs. elaidic acid, the trans olefinic protons are downfield from the cis protons in the two sets, external and internal protons. Similarly, the signals of the allylic protons of the cis isomers are downfield from the trans isomers, especially visible in the spectrum of the mixed Z,E isomer. In the case of identical double bond configuration, the signals of the two internal olefinic protons overlap as do the signals of the two external olefinic protons.
The 1H-NMR analysis of the compounds depicted here was also described in the literature (Lie Ken Jie et al., 1997; Lie Ken Jie, 2001). The corresponding data (also CDCl3, 300 MHz) are:
- Four peaks for the 9Z,11E isomer, namely, two multiplets (5.32, 5.65) and two triplets (5.82, 6.24) attributable to the outer (9, 12) and inner (10, 11) protons, respectively.
- For the 9Z,11Z isomer, a multiplet at 5.40 ppm assigned to the outer positions 9, 12 and a double of doublet 6.22 caused by the inner positions 10, 11.
- In the 9E,11E isomer, the outer protons at 5.56 ppm and inner protons at 5.96 ppm.
Literature:
- Lie Ken Jie, M.S.F., Pasha, M.K. and Alam, M.S. Synthesis and nuclear magnetic resonance properties of all geometric isomers of conjugated linoleic acids. Lipids, 32, 1041-1044 (1997).
- Lie Ken Jie, M.S.F. Analysis of conjugated linoleic acid esters by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol., 103, 628-632 (2001).
In This Section
- Introduction of NMR
- Saturated Fatty Acids and Methyl Esters
- Alkyl Esters Other than Methyl
- Glycerol Esters
- Non-Conjugated Double Bonds
- Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA)
- Acetylenic Fatty Acids and Derivatives
- Branched-Chain and Cyclic Fatty Acids
- Epoxy Fatty Acids
- Hydroxy and Hydroperoxy Fatty Acids
- Oxo Fatty Acids
- Fatty Alcohols
- Some Miscellaneous Fatty Acids
- Quantification by 1H-NMR
- The NMR Spectrum
- Alkanoic Acids
- Monoenoic Acids
- Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
- Non-Methylene-Interrupted Polyenoic Fatty Acids
- Acids with conjugated unsaturation
- Acetylenic and Allenic Acids and Esters
- Branched-Chain and Cyclic Fatty Acids
- Cyclic Fatty Acids
- Epoxides and Acyclic Ethers
- Hydroxy and Hydroperoxy Acids
- Oxo (Keto) Acids
- Acids, Esters (Alkyl, Glycerol, Waxes), Alcohols and Acetates, Amides, and Nitriles
- Esters of Glycerol and Other Polyhydric Alcohols
- Oils and Fats
- Regiospecific Analysis of Triacylglycerols